article: ingredient focus: marula

ingredient focus: marula

the bottom line
The marula plant has played an important role in southern Africa for centuries. Used for its durable wood, nutrition, and medicinal properties, it symbolizes the resilience and beauty of Africa. In the west, we honor marula for its use in care of the skin for both moisturization and anti-aging. Keep reading to learn more about this “tree of life”.
first layer: the history of marula
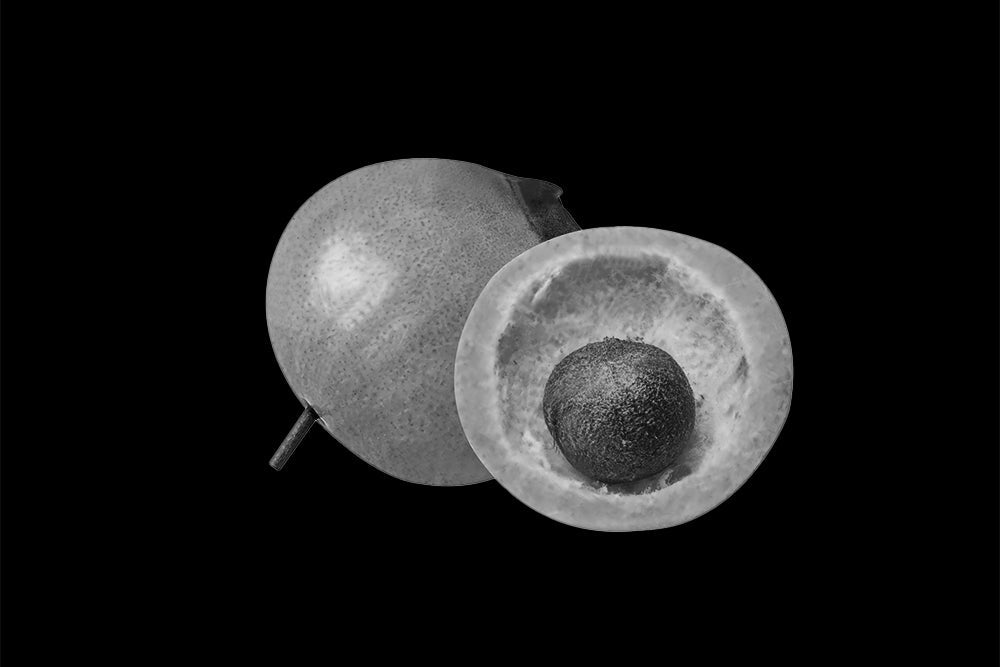
The marula tree (Sclerocarya birrea) is distributed throughout southern Africa, including South Africa, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Zambia, and Namibia. Archaeological finds in Zimbabwe demonstrate that marula fruit was consumed as far back as 10,000 BC. The tree has great spiritual significance and is regarded as a symbol of strength and endurance, with its branches believed to represent the human spirit. Rich in vitamin C, the fruit’s pulp provides essential nutrients in addition to oil extracted from the kernels. Although marula is commonly believed to responsible for the intoxication of elephants who feast on the fallen fruit, this is a pleasant myth. Nonetheless, marula fruit is believed to bring good fortune.
The bark of the marula tree also has value. It has been used to make clothing, while the wood itself is used in the fabrication of furniture and musical instruments. The oil from the kernel of the marula fruit is commonly used for cosmetics, including moisturization of the skin and hair, while the leaves have traditionally been used to treat acne as well as other skin conditions.
second layer: the science of marula
Marula is a significant medicinal plant. Various parts of the plant have been used for a myriad of medical treatments, with reported anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, and anticonvulsant effects. The use of marula for care of the skin is also well-documented. The saturated and unsaturated fatty acids within marula oil are very similar to those present in the epidermis, and include oleic acid (69%), palmitic acid (15.3%), linoleic acid (9.2%), palmitoleic acid (4.1%), and stearic acid (1.5%).
A clinical study evaluating the use of marula oil for skincare showed that it is non-irritating, moisturizing, hydrating, and occlusive. It’s also been reported to improve skin smoothness and decrease redness, while decreasing the level of transepidermal water loss (TEWL)*.
Extracts from the stem of the marula plant additionally have great value. One in vitro study showed that marula stem extract exhibited both anti-elastase* and anti-collagenase* activity, while extracts from the leaf demonstrate moderate anti-elastase activity. Compounds identified within marula stems include quinic acid, which has antioxidant*, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and anti-viral properties; and the polyphenols* epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), and epicatechin gallate (ECG), which have potent antioxidant effects.
Finally, marula possesses antibacterial activity; extracts from the stems and leaves have shown efficacy against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterococcus faecalis.
third layer: marula and skin care
Given these scientific properties, it’s not surprising that marula has several potential benefits in care of the skin.
- anti-aging: skin aging is accelerated by degradation of components of the extracellular matrix (ECM)*, including the proteins collagen and elastin. By inhibiting the enzymes that break these proteins down, i.e., collagenase and elastase, marula helps to limit aging of the skin.
- anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects: a reminder about free radicals - these creatures create oxidative stress and an inflammatory response which in turn can damage DNA, resulting in injury to the epidermis and dermis. This manifests as premature aging, with increased skin wrinkling, age spots, and skin laxity. Anti-inflammatories help to tone down the response, while antioxidants stabilize free radicals to limit how much damage they can do.
- hydration: marula oil is appreciated for its ability to gently hydrate and moisturize skin.
- skin barrier: when inflammation of the skin is present, there is decreased hydration of the stratum corneum and increased TEWL. By acting as an occlusive and helping to decrease TEWL, marula oil supports skin barrier function.
fourth layer: how we do it
Marula is an essential component of our ceramide restorative hand crème. Developed to soothe and hydrate the hands of our founder Dr. Naidu immediately following surgery, this crème was formulated to absorb quickly and help restore the skin barrier of the hands, without any sticky or waxy residue. Layered with mango butter, ceramide NP, marula oil, allantoin, calendula, and amaranth, it's a (yellow) green juice for your hands.
All this and more at anokhaskincare.com .
xx
anokha
references:
Komane B, Vermaak I, Summers B, Viljoen A. Safety and efficacy of Sclerocarya birrea (A.Rich.) Hochst (Marula) oil: A clinical perspective. J Ethnopharmacol 2015; 24(176): 327-335.
Shoko T, Maharaj VJ, Naidoo D, Tselanyane M, Nthambeleni R, Khorombi E, Apostolides Z. Anti-aging potential of extracts from Sclerocarya birrea (A. Rich.) Hochst and its chemical profiling by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. BMC Complement Altern Med 2018; 18(1):54.
Ojewole JA, Mawoza T, Chiwororo WD, Owira PM. Sclerocarya birrea (A. Rich) Hochst. ['Marula'] (Anacardiaceae): a review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology and its ethnomedicinal uses. Phytother Res 2010; 24(5):633-9.
Braca A, Politi M, Sanogo R, Sanou H, Morelli I, Pizza C, De Tommasi N. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds from wild and cultivated Sclerocarya birrea (Anacardiaceae) leaves. J Agric Food Chem 2003; 51(23): 6689-6695.
Gruenwald J. Anti-aging nutraceuticals. Food Sci Tech Int 2006; 20: 50-51.
Lall N, Kishore N. Are plants used for skin care in South Africa fully explored? J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 153: 61-84.
Eloff JN. Antibacterial activity of marula (Sclerocarya birrea (A. rich) Hochst. subsp. caffra (Sond.) Kokwaro) (Anacardiaceae) bark and leaves. J Ethnopharmacol 2001; 76(3): 305-308.
*definitions:
antioxidant: an antioxidant is a compound that inhibits oxidation. free radicals create oxidative stress and an inflammatory response which in turn can damage DNA and result in injury to the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin. in the skin, this manifests as premature aging with decreased elasticity leading to increased wrinkling, age spots, and decreased skin tone. antioxidants stabilize free radicals, which in turn limits their ability to damage the body.
collagenase: an enzyme that breaks the peptide bonds in collagen
elastase: a class of enzymes that cleaves peptides in elastin
extracellular matrix (ECM): a three-dimensional network of macromolecules and minerals outside of the cells, including collagen, enzymes, proteins, and hydroxyapatite. the ECM provides structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells.
polyphenol: large family of naturally occurring phenols which are abundant in plants. they include flavonoids and phenolic acids. they are known for their antioxidant properties.
TEWL: “transepidermal water loss”, or TEWL, is the normal movement of water from the stratum corneum to the atmosphere.
faq’s:
what is marula?
marula is a tree found in sub-Saharan Africa. also known as the “tree of life”, the marula tree has great spiritual significance and is regarded as a symbol of strength and endurance.
what are the benefits of Sclerocarya birrea?
Sclerocarya birrea, or marula, provides benefits to the skin and hair, including moisturization, antioxidant protection, and anti-inflmmatory effects.
do elephants really become drunk from eating fruit of the marula tree?
no, elephants do not actually become intoxicated by the fruit of the marula tree, although it’s a cute myth.

leave us a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.